Understanding Medium Voltage Switchgear
What is Medium Voltage in Electrical Engineering
In electrical systems, medium voltage (MV) refers to the range between 1 kV and 36 kV. It is widely used for power distribution in utilities, industrial plants, and renewable energy facilities.
Definition of Medium Voltage Switchgear
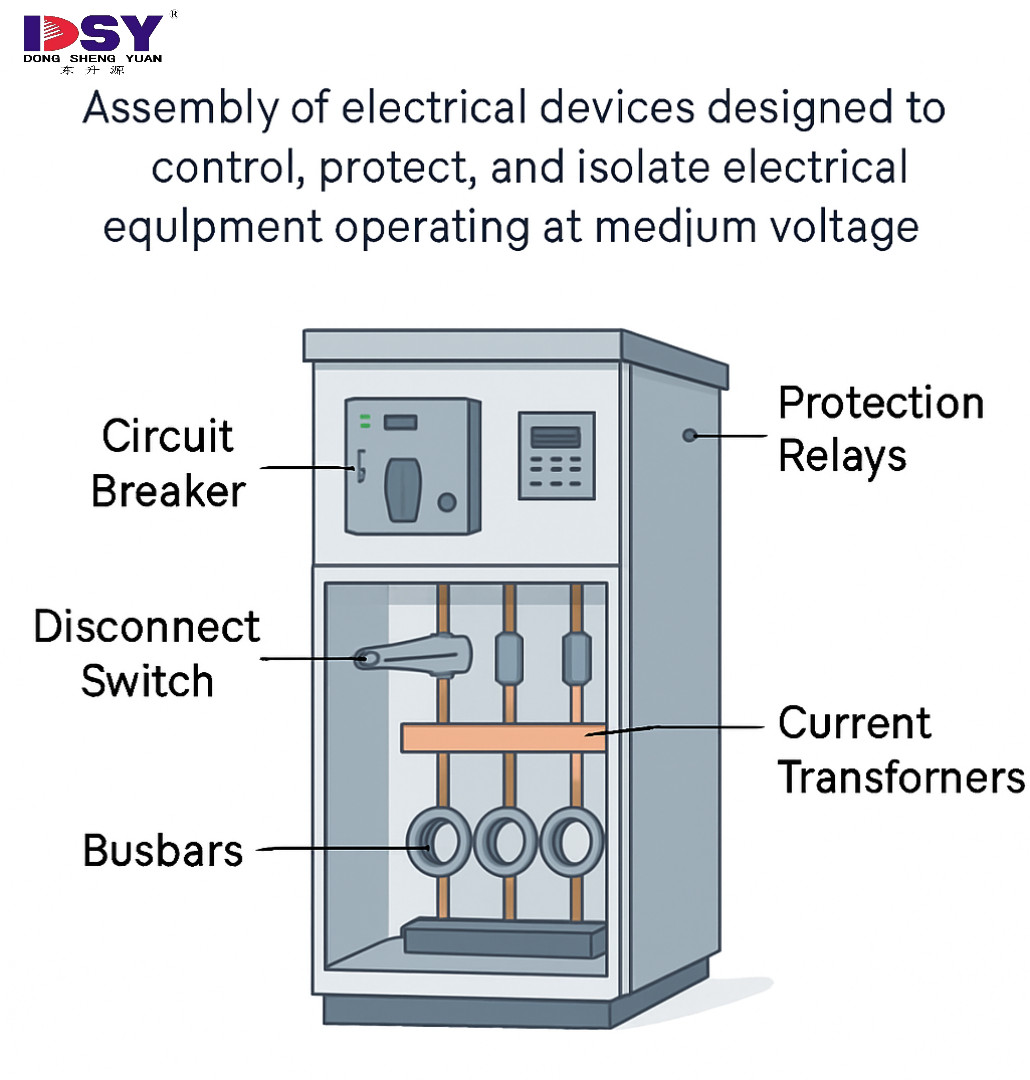
Medium voltage switchgear is an assembly of electrical devices—including circuit breakers, disconnect switches, busbars, and relays—designed to control, protect, and isolate electrical equipment operating within the MV range.
Why Medium Voltage Switchgear Matters
Ensuring Safety in Power Systems
Medium voltage switchgear plays a critical role in protecting both people and equipment from electrical hazards. It detects faults instantly and disconnects affected sections before damage occurs.
Supporting Industrial and Utility Networks
In utility grids, MV switchgear ensures stable power delivery to cities and industrial zones, while in factories, it safeguards expensive machinery from electrical faults.
Components of Medium Voltage Switchgear
Circuit Breakers and Disconnectors
-
Circuit breakers interrupt electrical faults by breaking the circuit.
-
Disconnectors safely isolate equipment for maintenance.
Busbars, CTs, and Protection Relays
-
Busbars distribute electricity between incoming and outgoing circuits.
-
Current transformers (CTs) measure electrical current for monitoring.
-
Protection relays trigger breakers when faults are detected.
How Medium Voltage Switchgear Works

Normal Operating Conditions
During normal operation, MV switchgear channels electricity from the supply source to various load circuits, ensuring stable voltage and current flow.
Fault Detection and Isolation
When a fault occurs:
-
Protection relays detect abnormal current or voltage.
-
Circuit breakers trip, isolating the faulty section.
-
Power continues flowing to unaffected sections.
Restoration After Fault Clearance
Once maintenance is completed:
-
The fault section is reconnected.
-
Circuit breakers are reset.
-
The system resumes normal operation.
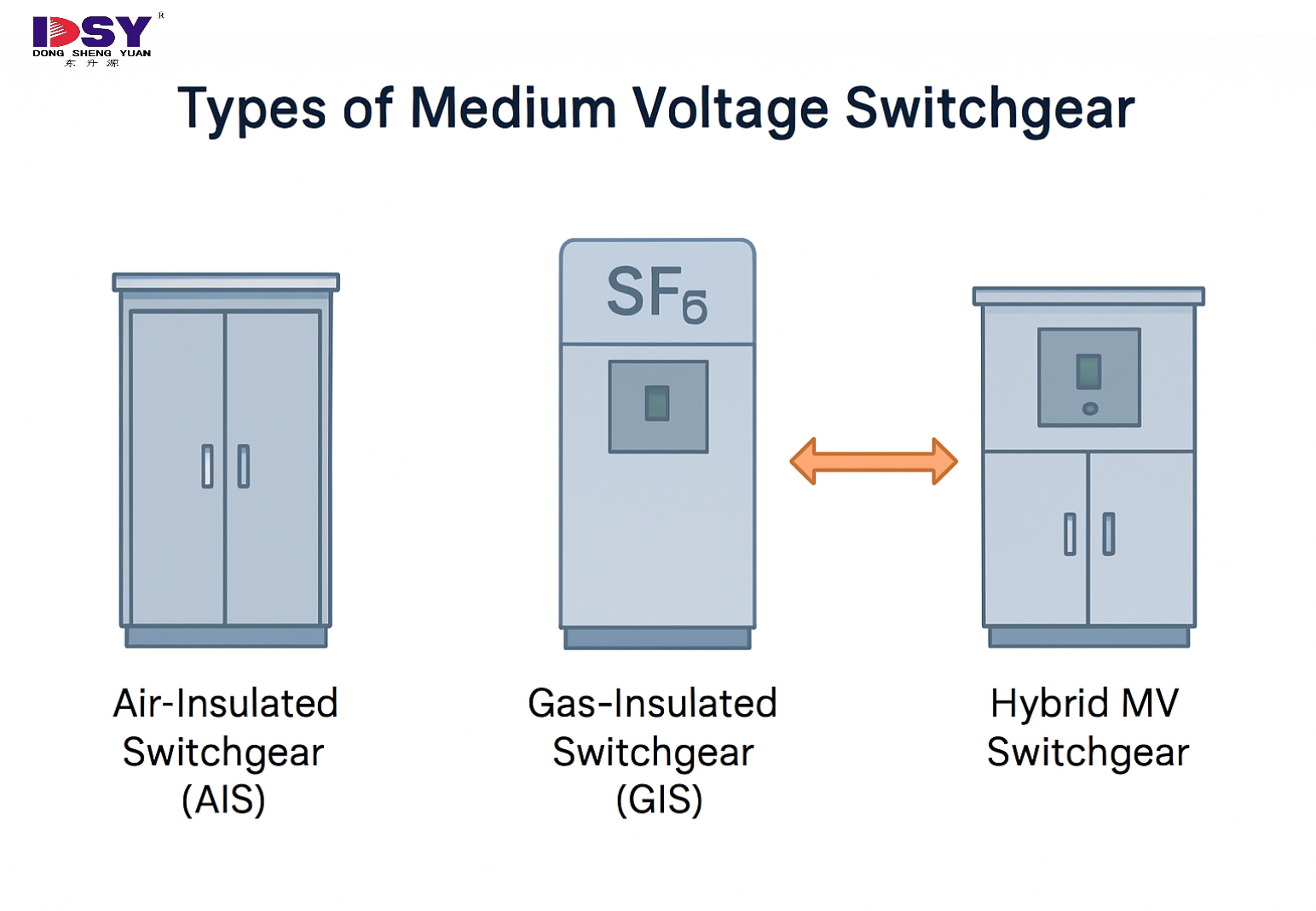
Types of Medium Voltage Switchgear
Air-Insulated Switchgear (AIS)
-
Uses air as the insulation medium.
-
Common in indoor substations and industrial sites.
Gas-Insulated Switchgear (GIS)
-
Uses SF₆ gas for insulation.
-
Compact and suitable for space-constrained environments.
Hybrid MV Switchgear
-
Combines AIS and GIS technologies for flexibility and efficiency.
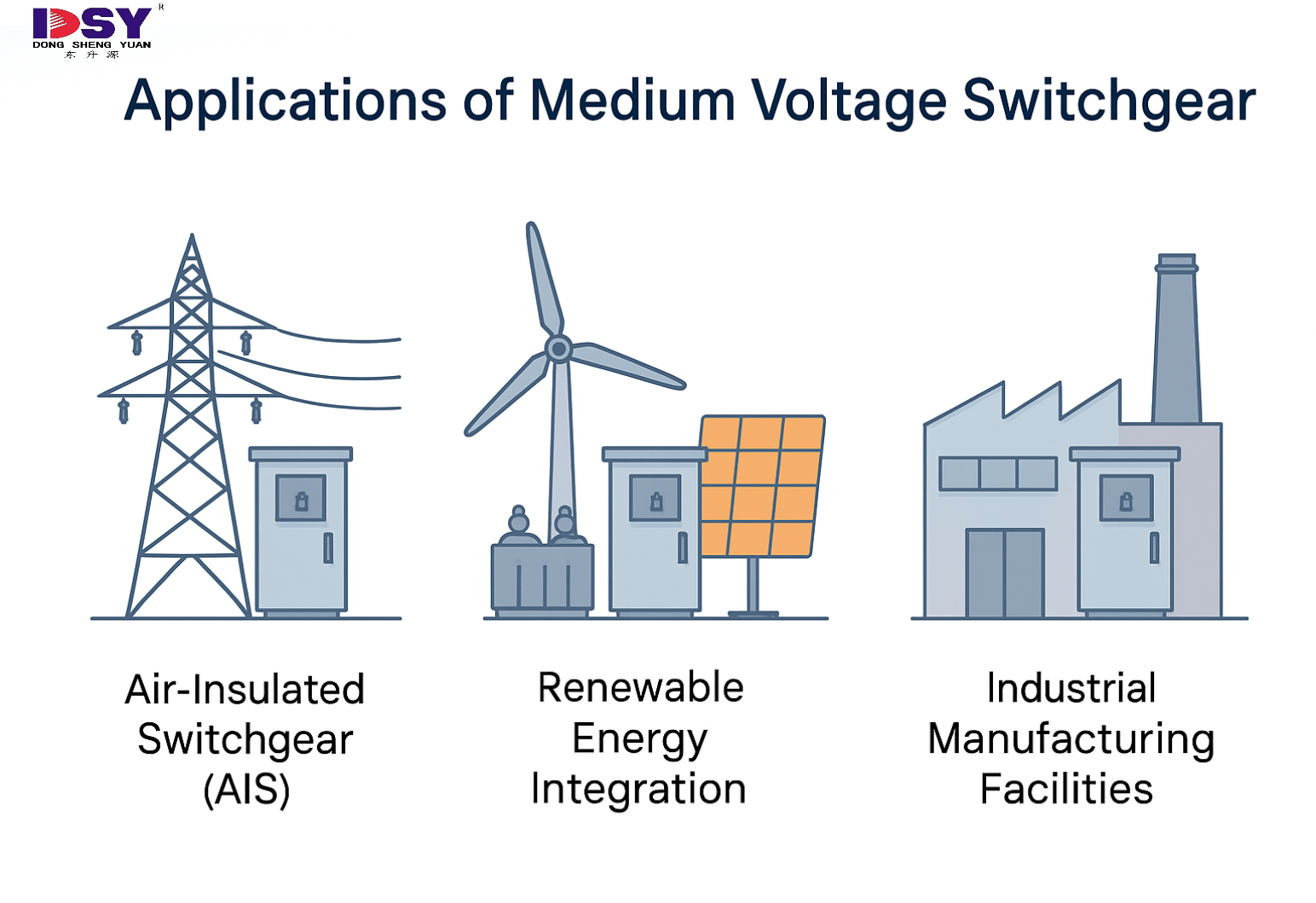
Applications of Medium Voltage Switchgear
Utility Substations
Facilitates the safe distribution of power from high-voltage transmission lines to lower-voltage distribution networks.
Renewable Energy Integration
Manages power output from wind and solar farms before feeding it into the grid.
Industrial Manufacturing Facilities
Protects heavy-duty machinery from overloads and short circuits.
DSY Solutions for Medium Voltage Switchgear
Dongshengyuan Electronic (DSY) offers customized medium voltage switchgear solutions engineered for safety, performance, and compliance.
Custom-Engineered MV Switchgear
-
Modular AIS, GIS, and hybrid configurations.
-
Designed for specific industrial or utility applications.
Compliance with IEC & IEEE Standards
DSY switchgear meets IEC 62271 and IEEE C37 standards, ensuring quality and global compatibility.
Learn more at dsyswitchgear.com
See standard guidelines at IEC Standards (external link)
FAQs About Medium Voltage Switchgear
Q1: What is medium voltage?
Typically between 1 kV and 36 kV, used in power distribution systems.
Q2: How does medium voltage switchgear work in a power system?
It controls, protects, and isolates equipment by detecting faults and disconnecting affected circuits.
Q3: What’s the difference between AIS and GIS switchgear?
AIS utilizes air insulation, while GIS employs gas insulation for a more compact design.
Q4: Where is MV switchgear used?
In substations, industrial plants, renewable energy projects, and large commercial facilities.
Q5: How long does MV switchgear last?
Typically 25–30 years with proper maintenance.
Conclusion: Why Understanding MV Switchgear Operation Matters
Knowing how medium voltage switchgear works is essential for electrical engineers, facility managers, and utility operators. It ensures systems remain safe, reliable, and efficient. With DSY’s advanced MV switchgear, you get solutions designed for today’s demanding power systems.
Visit dsyswitchgear.com to explore DSY’s MV solutions.