What is Medium Voltage?
Medium voltage is a fundamental classification in power systems that defines electrical equipment operating between 1 kilovolt (kV) and 36 kV. It plays a critical role in ensuring the safe and reliable distribution of electricity in various industrial and commercial infrastructures.
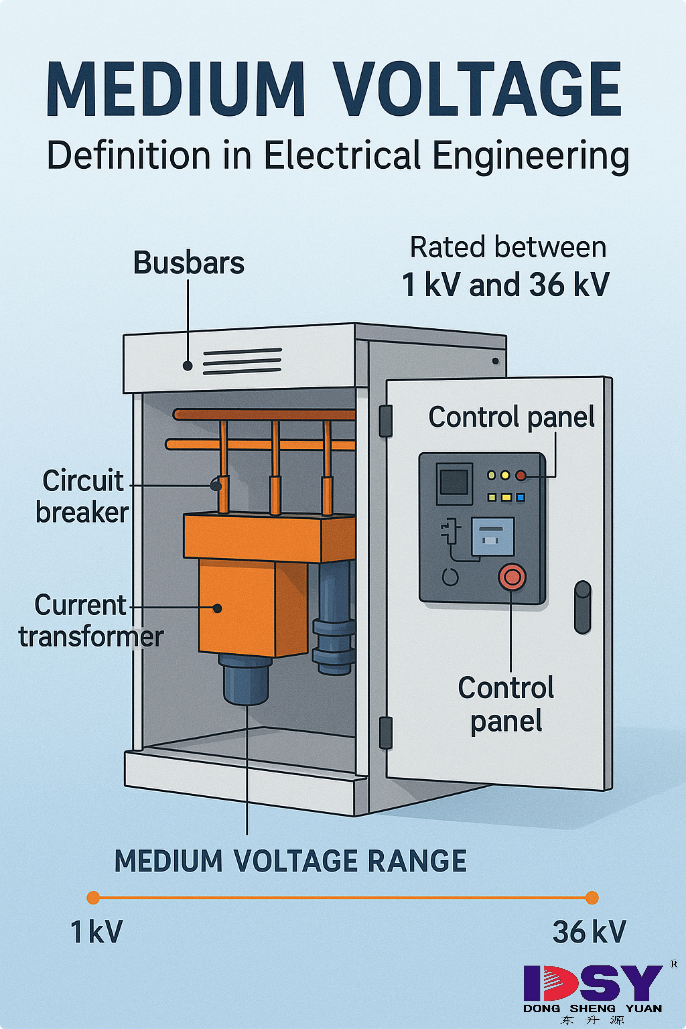
It acts as the bridge between low-voltage consumer systems and high-voltage transmission networks, handling distribution over long distances and ensuring proper control through devices like switchgear and transformers.
Switchgear Definition in Electrical Engineering
Switchgear refers to the devices used to control, protect, and isolate electrical circuits. In medium voltage systems, switchgear ensures fault protection and operational continuity in critical applications.
Voltage Classification Overview
Electrical voltages are typically categorized as:
-
Low Voltage (LV) – up to 1 kV
-
Medium Voltage (MV) – 1 kV to 36 kV
-
High Voltage (HV) – above 36 kV
Voltage Levels: Low, Medium, and High
Low Voltage (LV): Characteristics & Usage
-
Voltage: ≤ 1 kV
-
Used in homes, small offices, and devices
-
Safe for general public contact
Medium Voltage (MV): Where It Fits
-
Voltage: 1 kV to 36 kV
-
Used in commercial, industrial, and municipal grids
-
Requires professional handling and protective equipment
High Voltage (HV): Industrial Scope
-
Voltage: >36 kV
-
Used in bulk transmission over long distances
-
Limited to national grids and major power plants
Typical Range of Medium Voltage
Standard Ranges: 1 kV to 36 kV
Most global utilities classify medium voltage as 1 kV to 36 kV, although specific countries may define sub-ranges like:
-
3.3 kV
-
6.6 kV
-
11 kV
-
33 kV
International Standards (IEC, IEEE)
IEC 60038 and IEEE 1585 set the benchmarks for classifying medium voltage ranges in power system design and safety protocols.
Importance of Medium Voltage in Power Systems
Medium voltage bridges high-capacity transmission systems and user-level distribution networks. It enables:
-
Efficient long-range power delivery
-
Fault isolation through automated systems
-
Cost-effective voltage step-down using transformers
Role in Distribution and Control
MV equipment is widely used in substations to step down voltage from transmission lines before sending it to cities, industrial parks, or commercial hubs.
Medium Voltage vs Low Voltage Distribution
| Feature | Medium Voltage | Low Voltage |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Range | 1 – 36 kV | ≤ 1 kV |
| Applications | Grids, factories | Homes, devices |
| Equipment | Switchgear, relays | Fuses, breakers |
| Risk & Handling | Requires PPE, training | General safety |
Medium Voltage Applications Across Industries

Utility Grids and Distribution Lines
Ensures controlled distribution from power plants to cities via substations.
Renewable Energy & Smart Grids
Used in wind farms and solar plants to manage energy flow into national grids.
Infrastructure: Airports, Hospitals, Data Centers
Guarantees reliable electricity in mission-critical operations.
Common Medium Voltage Equipment
-
Medium Voltage Switchgear – Protects and distributes power
-
Circuit Breakers – Interrupt faults
-
Transformers – Step-down or step-up voltage levels
-
Busbars & Cables – Distribute power across units
DSY Solutions for Medium Voltage Applications
Dongshengyuan (DSY) specializes in medium voltage systems, offering tailored switchgear and integrated power management solutions.
Medium Voltage Switchgear from DSY
-
Certified to IEC 62271 and IEEE C37 standards
-
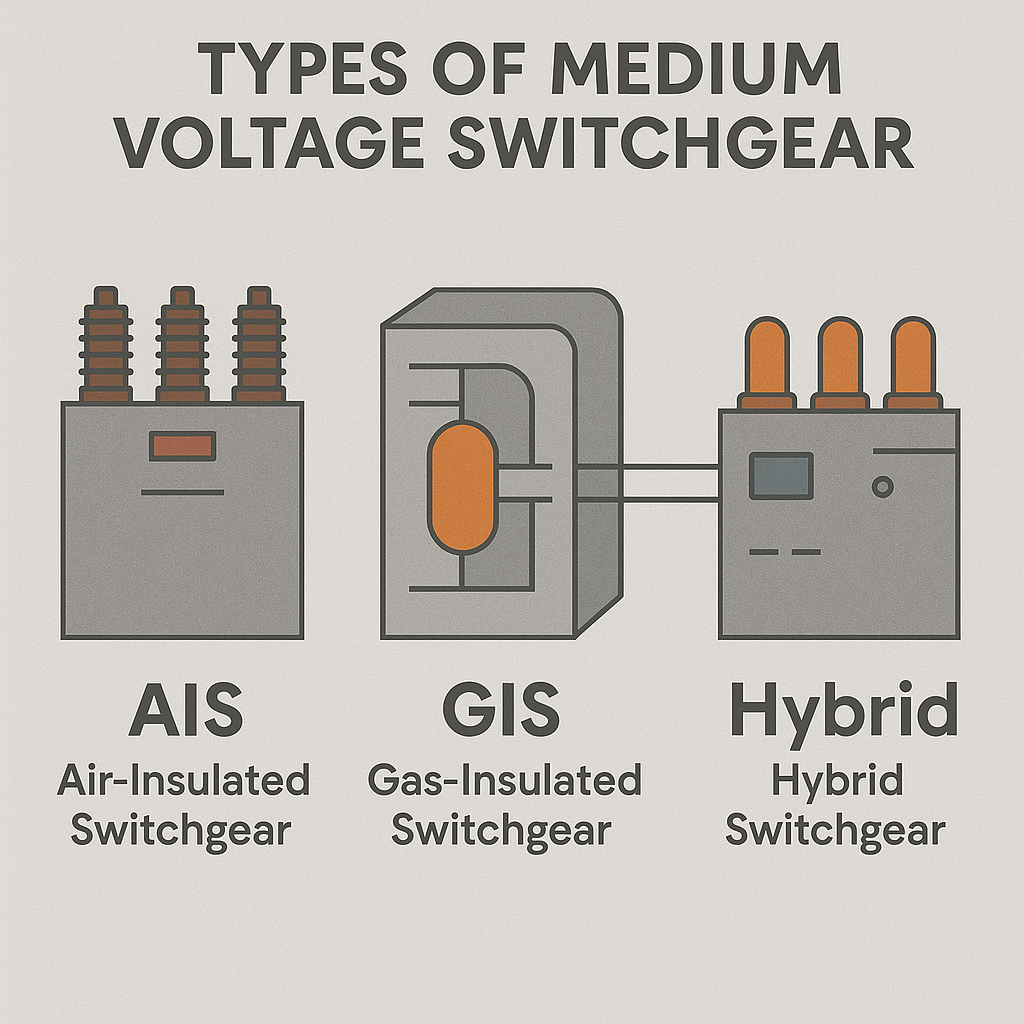
Available in AIS, GIS, and hybrid models
-
Integrated with smart monitoring capabilities
Custom Engineering and Safety Standards
DSY products are designed with safety, scalability, and efficiency in mind — ideal for large-scale grid systems and industry-specific needs.
Learn more at dsyswitchgear.com
FAQs about Medium Voltage
Q1: What voltage is considered medium voltage?
Typically from 1 kV to 36 kV, depending on regional standards.
Q2: What equipment uses medium voltage?
Switchgear, transformers, circuit breakers, relays, and substations.
Q3: Is medium voltage dangerous?
Yes. It requires special training and safety measures for handling.
Q4: Where is medium voltage applied?
In factories, airports, hospitals, wind farms, and grid substations.
Q5: What’s the difference between medium and high voltage?
High voltage is used for long-distance bulk transmission (above 36 kV), whereas medium voltage is for local distribution.
Conclusion: Why Medium Voltage Matters Today
From energy efficiency to smart grids, medium voltage is the unsung hero powering the world’s most vital systems. With DSY’s cutting-edge MV solutions, industries can count on safe, scalable, and standards-compliant power delivery.
Visit dsyswitchgear.com to explore DSY’s MV product lineup.